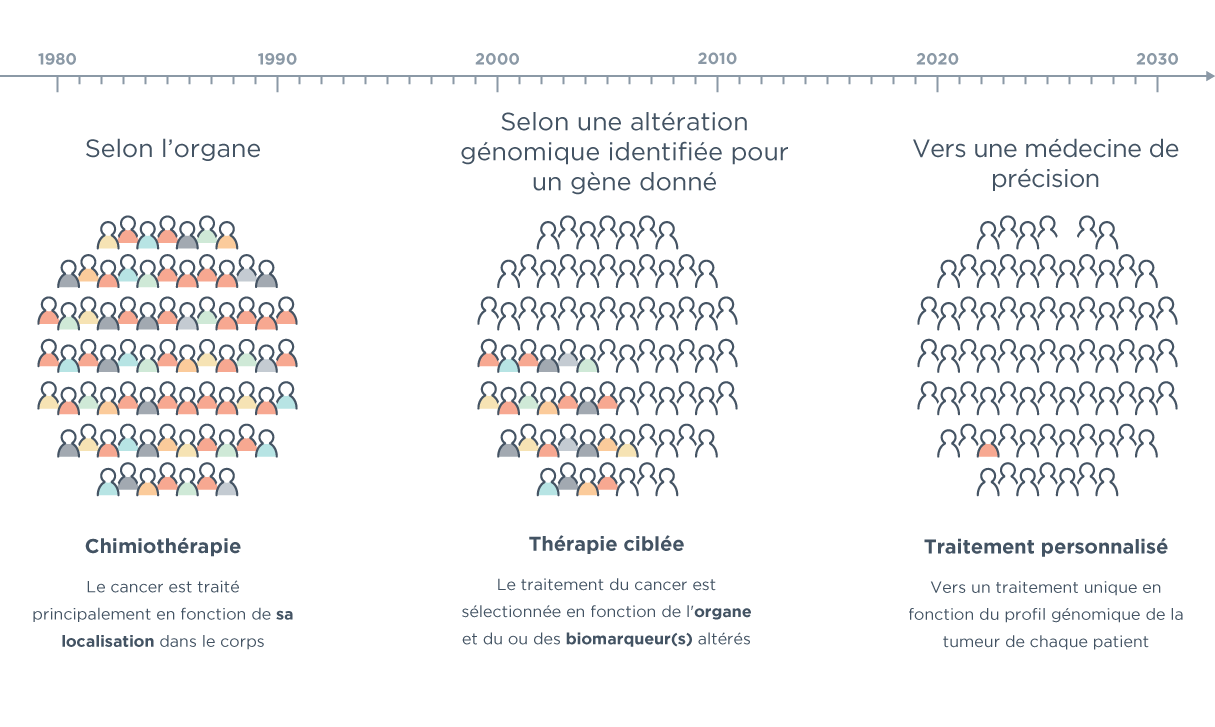
____________
FoundationOne®CDx, FoundationOne® Liquid CDx et FoundationHeme®, sont des dispositifs médicaux de diagnostic in vitro (DM-DIV).
Ce sont des produits réglementés qui portent, au titre de cette réglementation, le marquage CE.
Pour une information complète sur Foundation One®Cdx, Foundation One®Liquid Cdx, Foundation Heme®, veuillez consulter les spécifications techniques.
La décision d'effectuer un test Foundation One® est prise par l'oncologue responsable de la stratégie thérapeutique.
Les actes de séquençage haut débit (NGS) peuvent être financés dans le cadre du référentiel des actes innovants hors nomenclature (RIHN) selon les modalités fixées par la Direction Générale de l’offre de soin.
Foundation Medicine et Foundation One sont des marques déposées de Foundation Medicine.
Fabricant : Foundation Medicine®, Inc - 150 Second Street Cambridge, MA 02141, USA
Mandataire : Qarad b.v.b.a, Cipalstraat 3, 24400 Geel, Belgique
Distributeur autorisé en dehors des Etats-Unis : Roche SAS 4, cours de l'Ile Seguin, 92650 Boulogne Billancourt Cedex, France
- Rozenblum AB et al._ Clinical Impact of Hybrid Capture–Based Next-Generation Sequencing on Changesin Treatment Decisions in Lung Cancer_ J Thorac Oncol_2017; 12: 258–268.
- Schwaederle M et al._ Precision Oncology: The UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center PREDICT Experience_ Mol Cancer Ther_2016; 15: 743–752.
- Mansinho A et al._ The future of oncology therapeutics_ Expert Rev Anticancer Ther_2017; 17: 563–565.
- Frampton GM et al._Development and validation of a clinical cancergenomic profiling test based on massively parallel DNA sequencing_ Nat Biotechnol_2013; 31: 1023–1031.
- Drilon A et al._ Broad, hybrid capture-based next-generation sequencing identifies actionable genomic alterations in “driver-negative”lung adenocarcinomas_ Clin Cancer Res_2015; 21: 3631–3639.
- Hirsch FR et al._ New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer_Lancet_2016; 388: 1012–1024.
- Baumgart M._ New Molecular Targets on the Horizon in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer_ Am J Hematol Oncol_2015; 11: 10–13.
- Chakravarty D et al._ OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base_ JCO Precis Oncol_2017; doi: 10.1200/PO.17.00011. [Epub ahead of print].
- Global Oncology Trends Report 2018. Report by IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. Disponible sur : https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/global-oncology-trends-2018.pdf (Publié Octobre 2018).
- Gagan J, Van Allen EM._ Next-generation sequencing to guide cancer therapy_ Genome Med_2015; 7: 80.
- Schrock AB et al._ Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Identifies Frequent Drug-Sensitive EGFR Exon 19 Deletions in NSCLC not Identified by Prior Molecular Testing_ Clin Cancer Res_2016; 22: 3281–3285.
- Rankin A et al._ Broad Detection of Alterations Predicted to Confer Lackof Benefit FromEGFR Antibodies or Sensitivity to Targeted Therapy in AdvancedColorectal Cancer_Oncologist_2016; 21: 1306–1314.
- Suh JH et al._ Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Facilitates Implementation of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines for Lung Cancer Biomarker Testing and Identifies Patients Who May Benefit From Enrollment in Mechanism-Driven Clinical Trials_Oncologist_2016; 21: 684–691.
- Zhao P et al._ Mismatch repair deficiency/microsatellite instability-high as a predictor for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy efficacy_2019 J Hematol Oncol; 12: 54.
- Abida W et al._ Analysis of the Prevalence of Microsatellite Instability in Prostate Cancer and Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade_2019 JAMA Oncol; 5: 471–478.
- Kok M et al._ How I treat MSI cancers with advanced disease_2019 ESMO Open; 4(Suppl 2): e000511.
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Prostate Cancer. Version 2.2020, Mai 2020. Disponible sur: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf (Consulté Août 2020).
- FDA approval for first-line treatment of MSI-H/dMMR colorectal cancer. Disponible sur: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-first-line-treatment-msi-hdmmr-colorectal-cancer (Consulté Août 2020).
- FDA approval for adults and children with TMB-H solid tumors. Disponible sur: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-adults-and-children-tmb-h-solid-tumors (Consulté Août 2020).
- Gandara DR et al._ Blood-based tumor mutational burden as a predictor of clinical benefit in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with atezolizumab_2018 Nat Med; 24: 1441–1448.
- Yarchoan M et al._ PD-L1 expression and tumor mutational burden are independent biomarkers in most cancers_2019 JCI Insight; 4: e126908.
- Khagi Y et al._ Hypermutated Circulating Tumor DNA: Correlation with Response to Checkpoint Inhibitor–Based Immunotherapy 2017 Clin Cancer Res; 23: 5729–5736.
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 6.2020, Juin 2020. Disponible sur: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (Consulté Août 2020).
- Kalemkerian GP et al._ Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Patients With Lung Cancer for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/ International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/ Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Guideline Update_J Clin Oncol_2018; 36: 911–919.
- Lindeman NI et al_ Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors_ J Mol Diagn_2018; 20: 129–159.